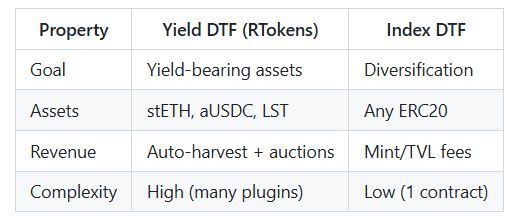
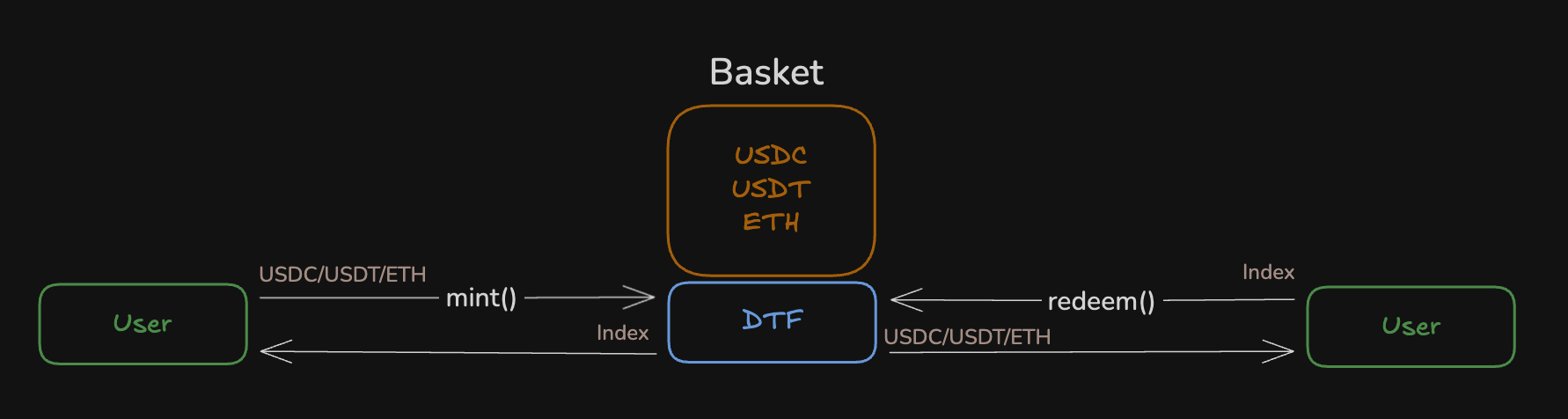
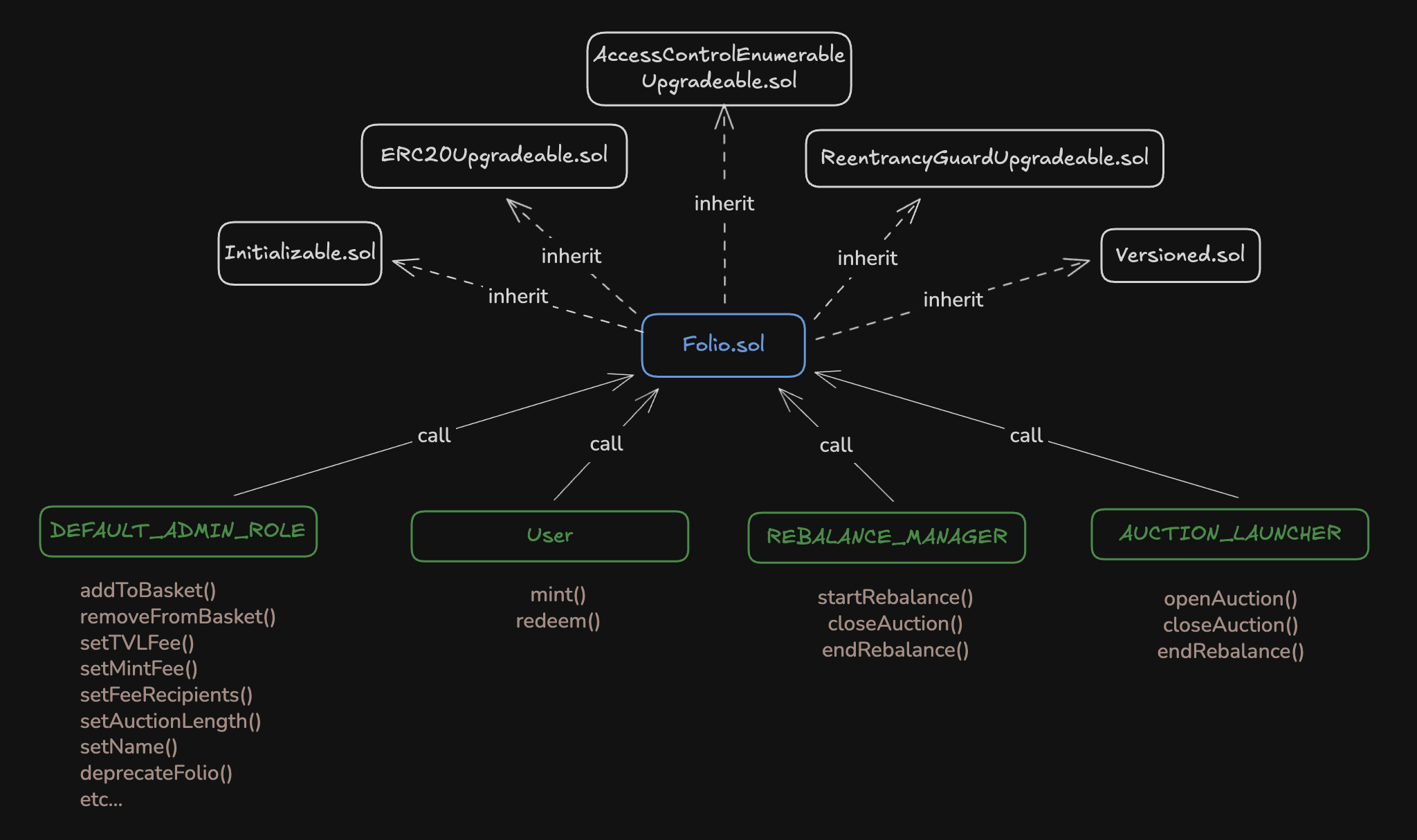
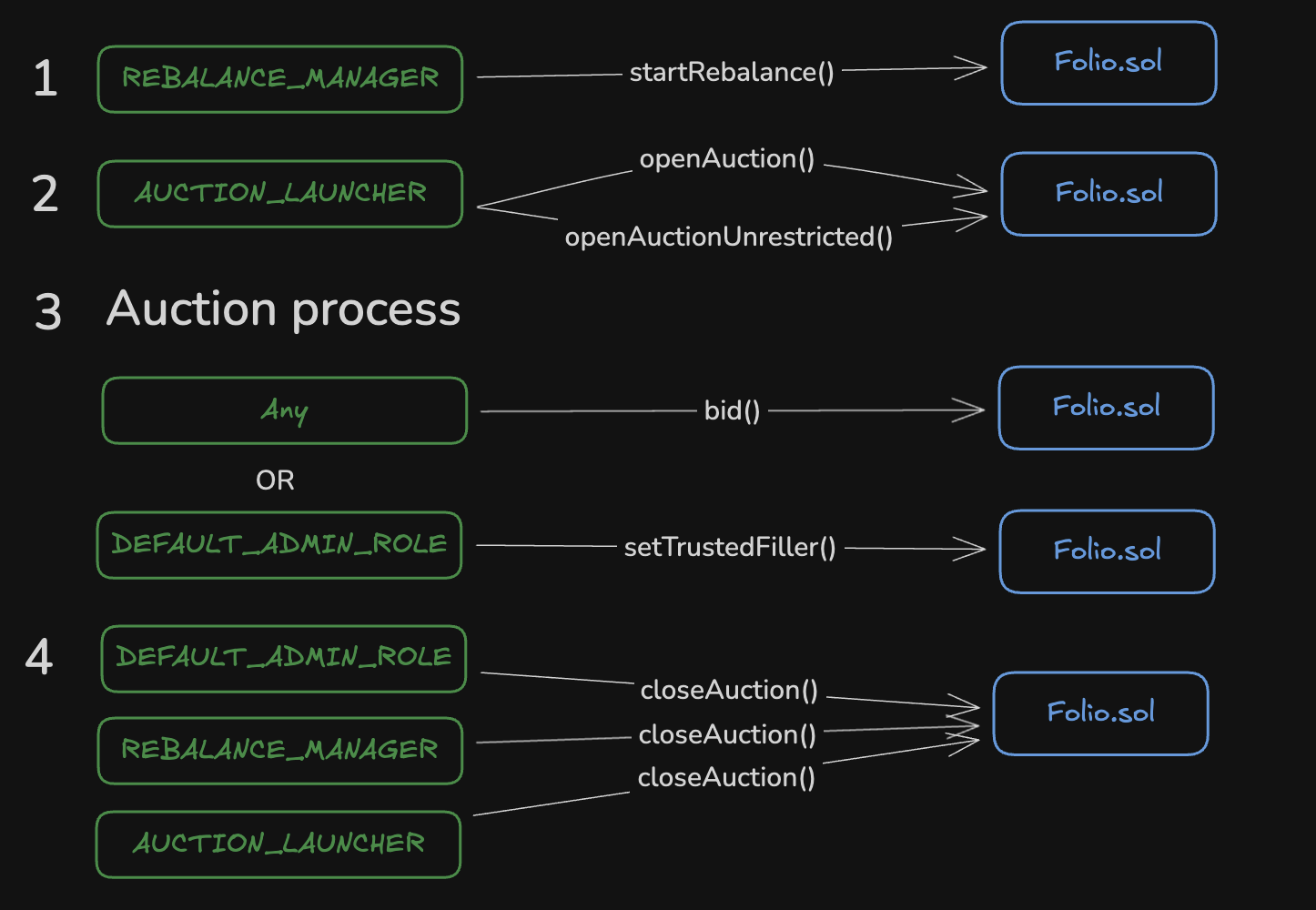
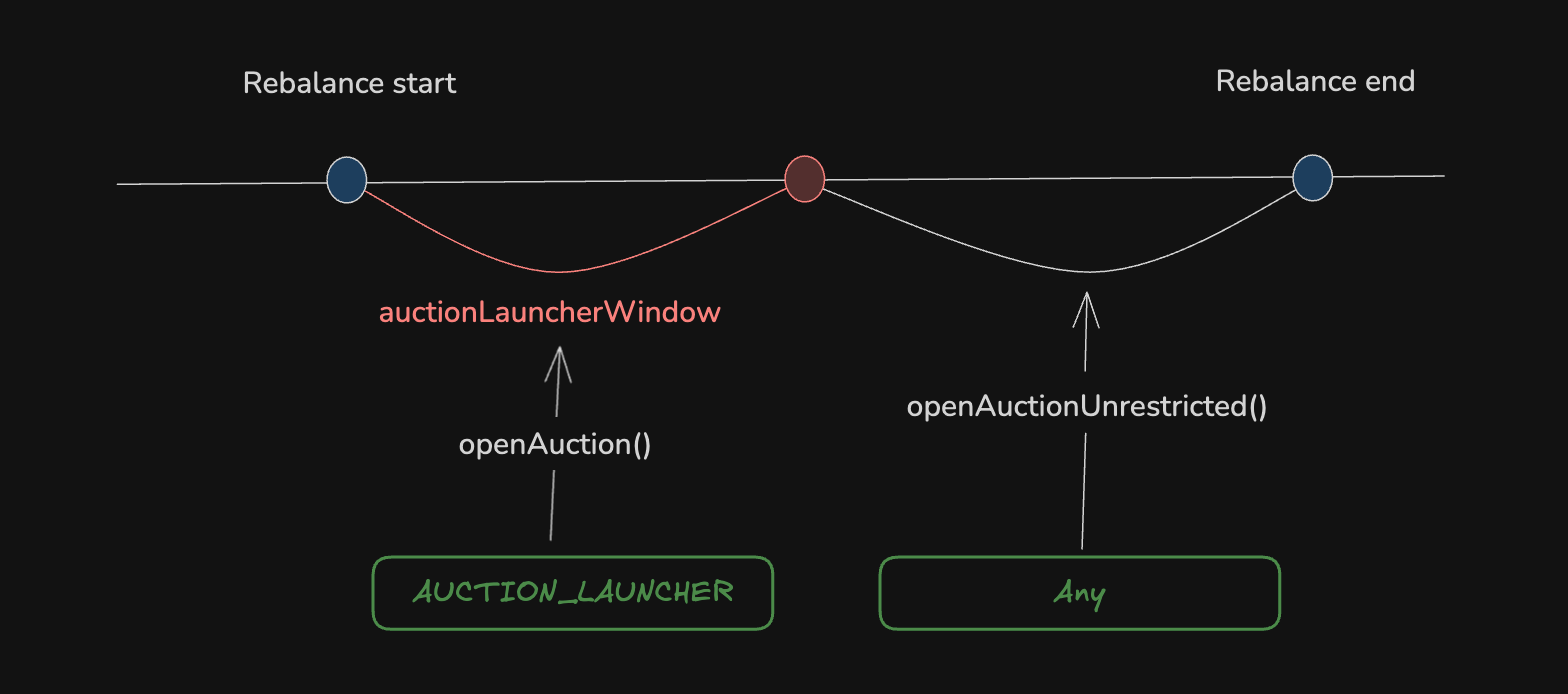
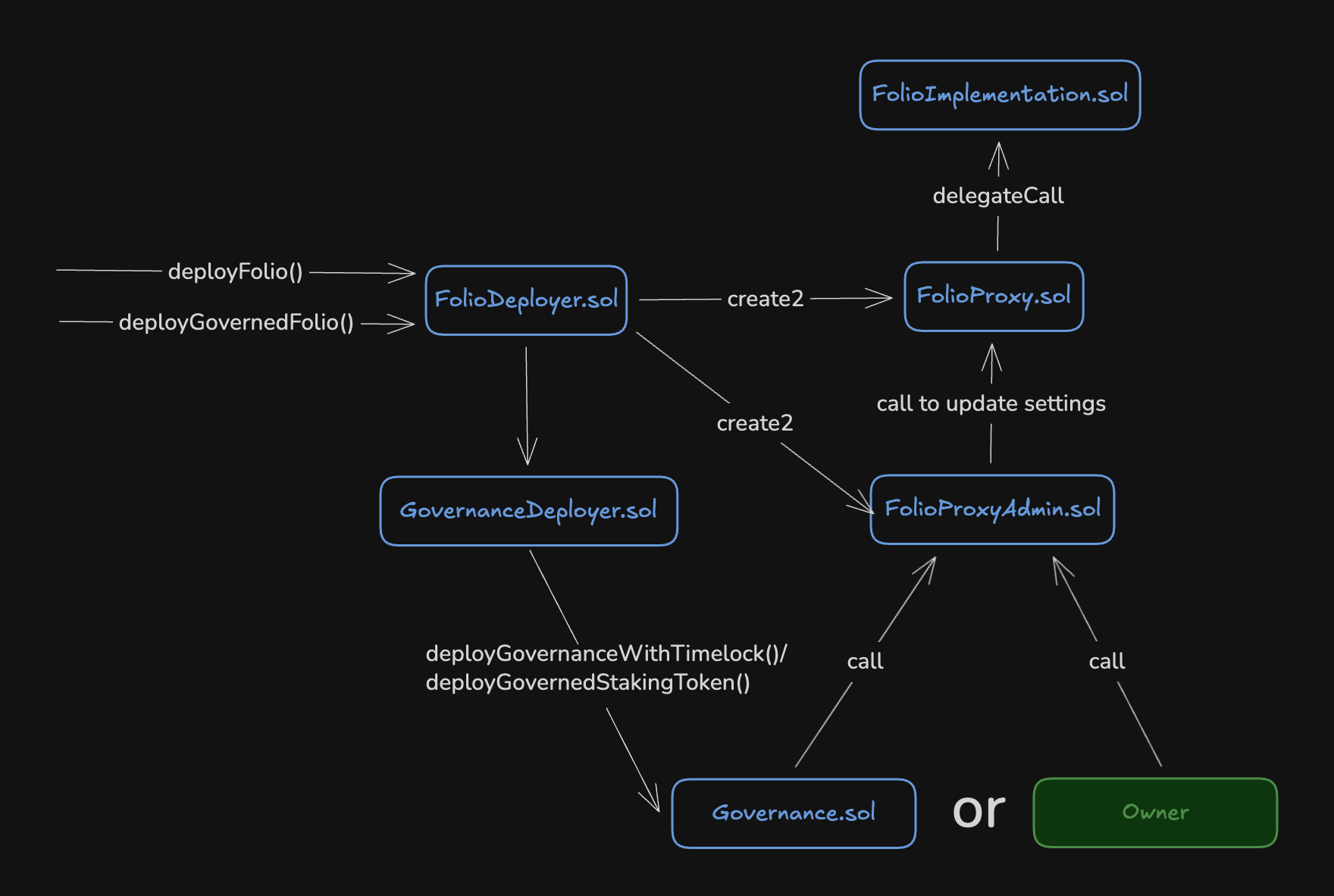
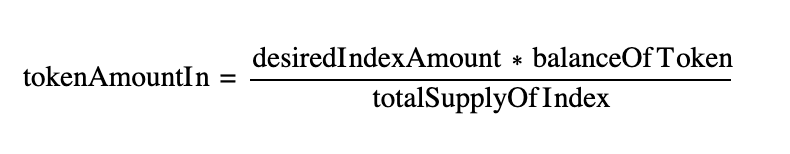The Reserve protocol carries risks for the user, and its documentation suggests reviewing them. Looking ahead, my opinion is that they are logical and not that critical. It’s just something you need to be aware of.
Smart Contracts
The protocol is built using smart contracts. If bugs or vulnerabilities are discovered in them, it could lead to the loss of user assets. The protocol's smart contracts have undergone several security audits, but no audit can guarantee total security. In my view, this risk is inherent to any DeFi application.
Oracle
For Yield DTFs, there is a risk associated with oracle performance. Oracles are used to obtain real-time price data to calculate the collateral amount.
Therefore, if a specific oracle erroneously reports the price of a collateral token, the DTF might consider the collateral to be in default and attempt to exchange it for emergency collateral, potentially at a loss.
Sandwich Attacks and MEV
MEV searchers constantly scan the blockchain for profit extraction opportunities. When interacting with any AMM-based DEX, users should consider slippage, which determines how much profit searchers can extract from a transaction.
It’s worth remembering that there are ways to protect against MEV via Flashbots RPC.
Governance Risks: Index Management via DAO
The protocol offers a management system for DTFs out of the box. It provides full on-chain governance. The system's powers are extensive, making attacks possible. These potential attacks could involve an attacker accumulating enough governance power to push through a malicious update, allowing them to steal funds.
These types of attacks are mitigated by the presence of specific roles in index management.
Admin Risks: Centralized Index Management
If a Default admin is used instead of governance for management, the administrator can:
- Remove a token from the basket, thereby freezing it.
- Stop minting (though redemption will still work).
- Upgrade to a malicious version (mitigated by the fact that the version must be in the versionRegistry).
- Shut down the index.
Collateral Asset Risks
Collateral asset risk is related to the fact that a collateral token might implement a blacklist that could include user addresses. This would make it impossible to get the "blacklisted" collateral token back, along with other tokens in the basket.
There are also some other risks that, in my opinion, are less interesting. For example, risks on the frontend part of the protocol which could be compromised, or the liability of other protocols whose tokens are used as collateral.