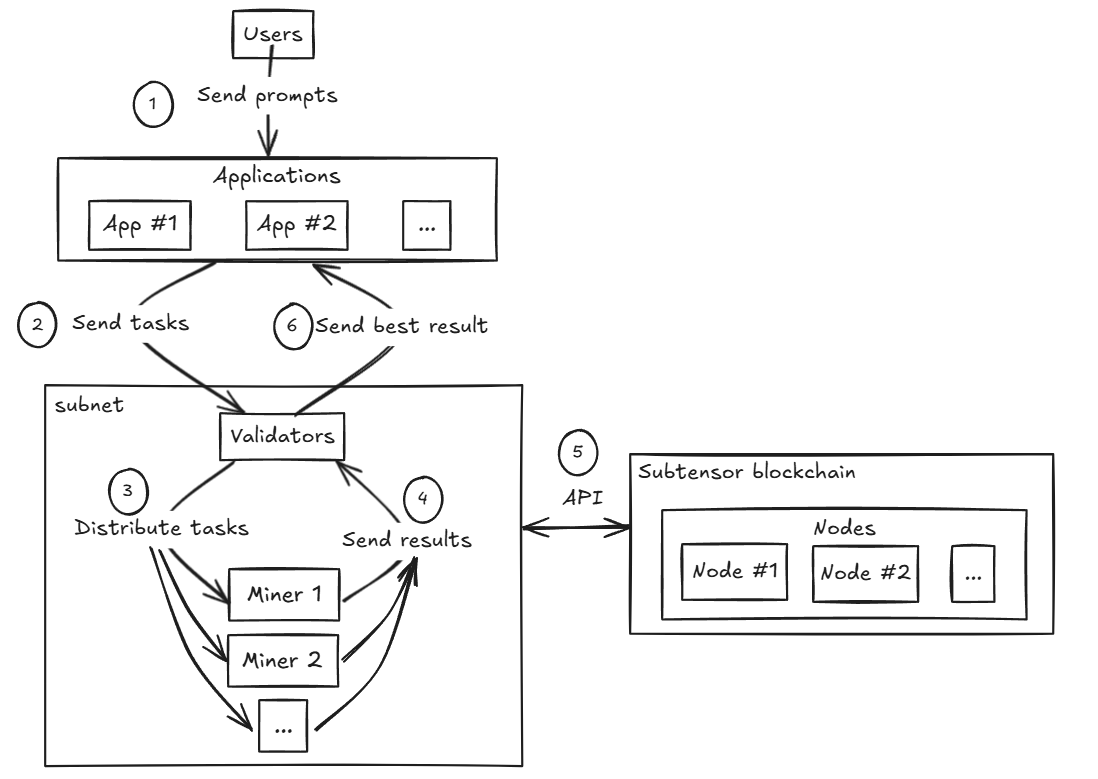
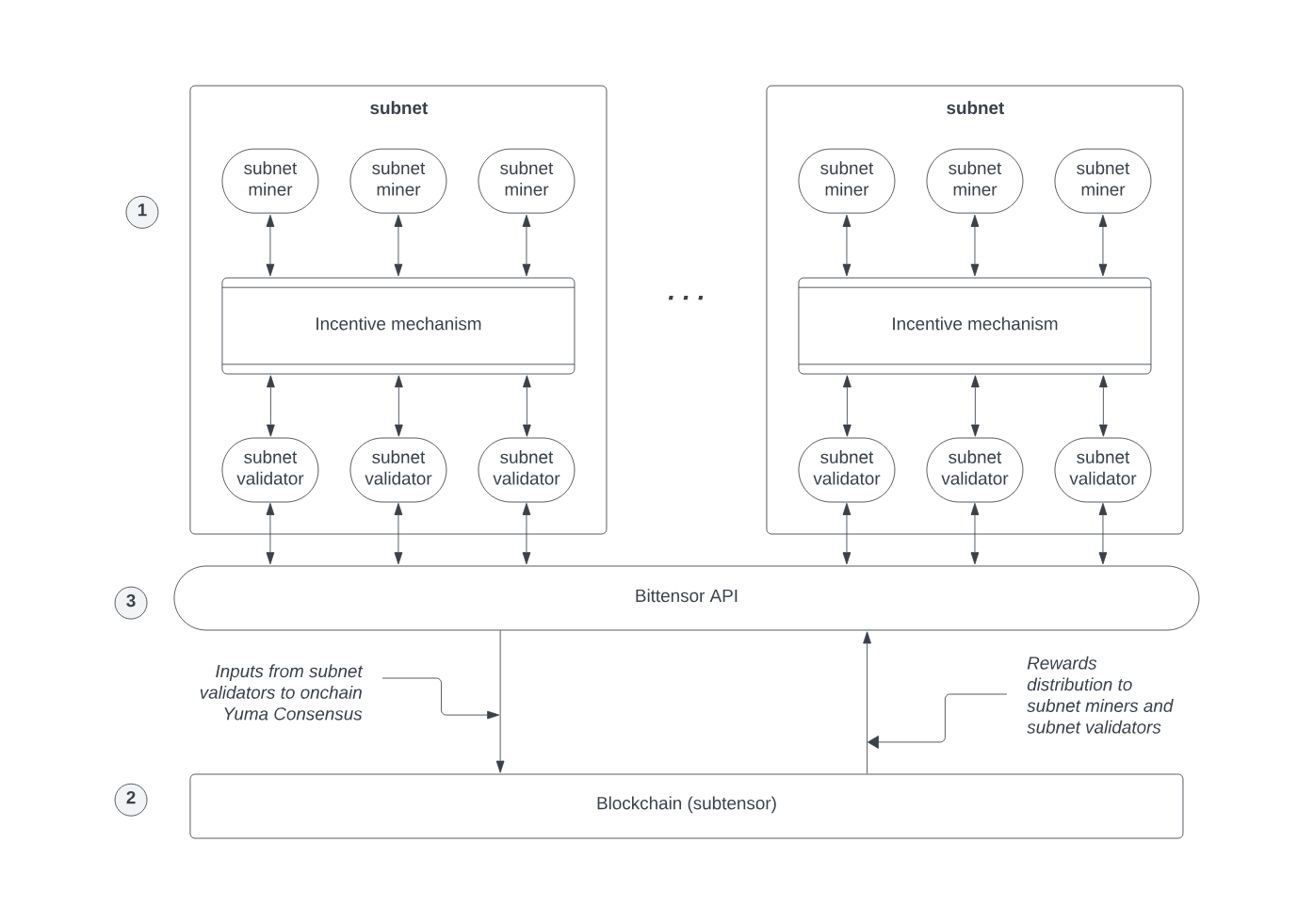
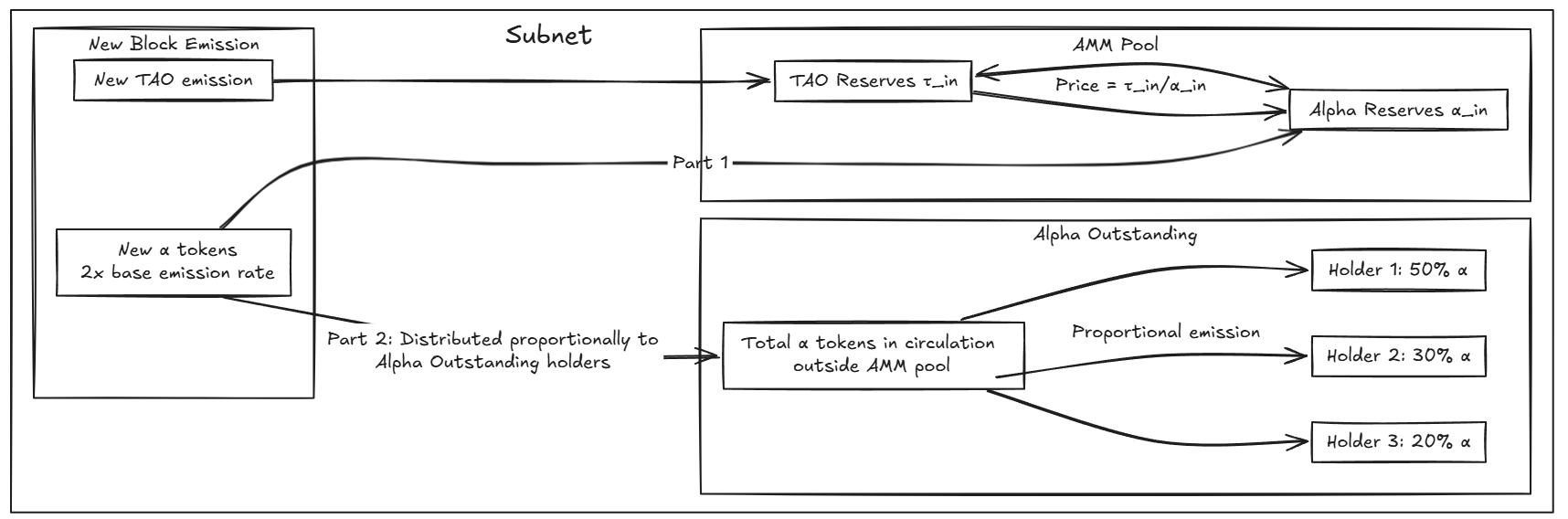
Bittensor has a unique architecture based on subnets, which allows for the creation of diverse and ambitious projects. Each subnet can be aimed at either commercial use or scientific research across various domains.
Subnet Categories
- Commercial Subnets: Offer services aimed at generating profit, for example, integrating miner outputs into third-party applications.
- Scientific Subnets: Support research in non-financial fields such as biology, medicine, and technology.
Our overview of subnets will include the top ones by market cap from this list.
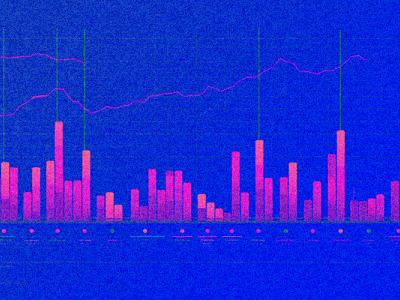
Let’s briefly talk about the dashboard interface using Subnet #64 as an example:
Let’s explain the chart and the buy/sell buttons.
As we mentioned earlier, each subnet is an AMM pool. The first asset is the TAO token, and the second is the subnet’s native token. The chart shows the price of the TAO token in the pool relative to the subnet token.
The value of the TAO token is regulated by the market. So when a subnet becomes popular or in demand, people deposit their TAO and withdraw the subnet token.
As a result, the amount of TAO in the pool increases, and the amount of the subnet token decreases.
As a result, the price of the subnet token increases.
Then all holders of the subnet token — miners, validators, stakers, and the subnet creator — can choose to exchange their reward tokens back into TAO, thereby realizing a profit.
In this way, a subnet’s AMM pool can be used for token swaps, staking, or cashing out profits for your work/contribution.
Let’s move on to reviewing subnets and their applications to understand how they can be used.
Subnet 19: Chutes — a subnet that provides access to various AI models through a unified API interface.
Chutes integrates both text models (like DeepSeek-R1 and others) and image generators (such as Dreamshaper XL, Stable Diffusion).
The main idea is that you can quickly deploy your own model or use already available public models — essentially an AI marketplace.
Applications built on the subnet:
Chutes.ai offers developers a simple REST API service to interact with public AI models, or the ability to deploy their own model to cloud storage and earn rewards when others use it.
Participation opportunities in the network:
- Miner:
- Provide computational resources to run AI models
- Handle user requests via the API
- Support various models (text generation, image generation, etc.)
- Earn rewards for processing requests
- Validator:
- Evaluate the quality and speed of miners' performance
- Check the availability and stability of provided services
- Monitor how well results match the requests
- Participate in distributing rewards among miners
- Consumer:
- Use the API to access various AI models
- Quickly deploy any public AI model from a large catalog, or your own model
- Access pre-deployed and optimized models via a simple API interface
- Transparent payment system: just top up your Bittensor blockchain address with TAO tokens
- Cost-efficiency: pay only for the actual compute used, no subscription fees or minimum charges
- No need for your own hardware to run resource-intensive AI models
- Ability to choose the most suitable models for specific tasks
Thus, Chutes is especially useful for both individual developers and companies that need flexible and scalable access to AI infrastructure without significant upfront investment.
Subnet 4: Targon — one of the largest subnets, where miners analyze responses from language models and provide sources to verify the accuracy of information using a deterministic verification mechanism.
Applications built on the subnet:
Sybil — an AI-powered search engine that delivers answers to user queries along with cited sources, ensuring a high level of result reliability.
Participation opportunities in the network:
- Miner:
- Process user queries using language models
- Search for and verify sources to support the information
- Provide structured answers with proper citations
- Support an API interface compatible with OpenAI standards
- Validator:
- Evaluate the accuracy and reliability of miners’ answers
- Check the relevance of the provided sources
- Monitor citation quality and how well answers match the queries
- Participate in reward distribution based on verification quality
- Consumer:
- Receive verifiable answers with cited sources
- Increased accuracy and reliability of results thanks to the verification mechanism
- Access to an OpenAI-compatible API for integration into your own applications
- Reduced reliance on centralized AI services while maintaining high-quality responses
- Protection against misinformation and unverified data through source-checking
- Use the API to integrate verifiable answers into your own apps
- Access trustworthy information with the ability to verify it
Thus, Targon and the Sybil.com platform built on it are especially valuable for users and developers who prioritize factual accuracy, as well as for companies looking to integrate verifiable AI-generated answers with sources into their products.
Subnet 8: Theta (PTN) — a specialized subnet that collects and analyzes trading signals from quantum models and deep learning systems to provide comprehensive trading recommendations across various asset classes.
Applications built on the subnet:
Taoshi — a platform offering access to high-precision trading signals generated by a decentralized network of algorithmic systems running on Bittensor infrastructure.
Participation opportunities in the network:
- Miner:
- Develop and run algorithmic trading models
- Generate trading signals across different asset classes
- Provide market movement forecasts with entry/exit levels
- Earn rewards based on the accuracy and effectiveness of signals
- Validator:
- Evaluate the historical accuracy of trading signals
- Monitor miner performance in real-time
- Verify whether signals align with market conditions
- Participate in reward distribution based on forecast performance
- Consumer:
- Access aggregated high-precision trading signals
- Get diversified trading signals across various asset classes (crypto, stocks, commodities, forex)
- Increased forecast accuracy through aggregation of data from multiple independent algorithmic systems
- Reduced risk through the use of diverse strategies and machine learning models
- Ability to integrate trading signals into your own trading systems via API, e.g., for use with trading bots
- Transparent signal performance tracking with historical data
- Access to diversified strategies from a wide range of algorithmic models
If you’d like, you can try creating an account and select free miners to test the service.
Thus, Theta is especially valuable for traders, investment funds, and financial institutions that need high-quality algorithmic trading signals without having to develop and maintain complex machine learning or quantum systems themselves.
Subnet 8: BitMind — a specialized subnet focused on identifying and verifying AI-generated content, using a decentralized network of miners to analyze and classify various types of media files.
Applications built on the subnet:
Thedetector — a platform for detecting AI-generated content, including images and videos, with high accuracy and transparent analysis results.
Participation opportunities in the network:
- Miner:
- Run detection algorithms for AI-generated content
- Analyze and classify various types of media files
- Continuously train and adapt to new content generation methods
- Earn rewards based on the accuracy of synthetic content detection
- Validator:
- Evaluate the accuracy of miners' detection models
- Verify results using benchmark datasets
- Monitor miners' ability to detect new types of AI-generated content
- Participate in reward distribution based on detection performance
- Consumer:
- Verify the authenticity of media files via web interface or API
- Reliably detect synthetic content (deepfakes, AI-generated images, texts, and audio) with high accuracy
- Continuously updated detection algorithms thanks to a decentralized network of miners adapting to new content generation methods
- Transparent verification process with detailed reports on indicators of artificial origin
- API integration into existing social media platforms, news sites, and content moderation systems
- Protection from disinformation and public opinion manipulation through detection of fake media
- Integration of verification tools into your own platforms
Thus, BitMind is especially valuable for media companies, social media platforms, law enforcement agencies, and fact-checking organizations that need reliable tools to combat disinformation and protect users from manipulative AI-generated content — in an era where the line between real and synthetic is becoming increasingly blurred.
Subnet 51: Compute Subnet — a decentralized P2P platform for renting GPU computing power, connecting GPU owners with users who need compute resources for various tasks.
Applications built on the subnet:
Celium Compute — a platform for renting computing power with a user-friendly web interface, where users can rent GPU resources directly from network miners.
Participation opportunities in the network:
- Miner (GPU Provider):
- Offer your GPUs for rent to other network participants
- Earn rewards for providing compute power
- Automatically manage workload and resource distribution
- Validator:
- Check the quality and availability of provided compute resources (remove miners if they don't maintain 100% uptime)
- Monitor fulfillment of rental agreements and handle disputes
- Participate in reward distribution among miners
- Earn rewards for validating operations in the network
- Compute Consumer:
- Access to a wide range of GPUs with varying performance levels
- Significant cost reduction for compute infrastructure
- Flexible payment and resource scaling system (payment via TAO token)
- Transparent pricing and participant reputation system
- No need for long-term contracts
- Access to specialized GPUs for machine learning and rendering tasks
- Option for short-term or long-term compute rentals
- Pay only for actual usage time
- Choose the optimal configuration for specific tasks
Thus, the Compute Subnet is especially valuable both for GPU owners looking to monetize idle hardware, and for companies, researchers, and developers in need of flexible access to compute power without large upfront hardware investments.
Subnet 19: Nineteen — a specialized subnet focused on building a decentralized network for handling complex text processing and generation tasks using LLMs. Unlike other subnets, Nineteen emphasizes executing specific instructions and tasks, rather than just generating generic text.
Applications built on the subnet:
Corcel — a platform providing an API for access to open-source language models with high performance and low latency. The service offers access to models like Llama 3, Mistral, and others via a simple, OpenAI-compatible API with pay-as-you-go pricing. Corcel focuses on delivering stable and fast infrastructure for developers who need reliable access to modern language models.
Tao Bot — a platform that simplifies access to the Bittensor ecosystem. Designed for both blockchain newcomers and experienced crypto enthusiasts, the service enables easy bridging, trading, and staking of tokens. Tao Bot abstracts the complexities of multichain interaction, allowing users to focus on exploring innovative AI networks and growing their digital assets. The main site is currently limited in functionality, but the protocol already has a working site.
Makeitaquote — a service for creating memes and quote images using various models.
Participation opportunities in the network:
- Miner:
- Run and maintain specialized language models optimized for instruction-following
- Process requests that require precise adherence to prompts and structured responses
- Execute complex tasks such as code generation, data analysis, and structured content creation
- Earn rewards based on instruction-following quality and output accuracy
- Validator:
- Evaluate miners’ ability to follow instructions and complete specific tasks
- Check the quality and structure of responses based on predefined criteria
- Monitor miner performance and their ability to handle various task types
- Participate in reward distribution based on objective metrics of instruction execution quality
- Consumer:
- Access to specialized language models optimized for following specific instructions
- Receive structured and accurate answers to complex queries
- Use models for practical tasks such as code writing, data analysis, and content creation
- Cost-efficiency: pay only for the compute actually used
- Increased reliability and precision in instruction execution compared to general-purpose language models
- Access to models specifically trained for narrow, task-focused applications
- Get results in a structured format, ready for integration into applications
Thus, Subnet Nineteen is especially valuable for developers, data analysts, and companies that require language models capable of accurately following instructions and performing specific tasks with a high degree of structure and precision.
Subnet 13: Data Universe — a specialized subnet designed for collecting, storing, and providing access to large volumes of data from various sources.
The subnet is built with a focus on decentralization and scalability, allowing up to 50 petabytes of data to be stored across 200 miners, while requiring only around 10 GB of storage on validators.
Applications built on the subnet:
Data Universe Dashboard — an information panel that displays the current state of data in the network, helping miners optimize their setup to maximize rewards.
HuggingFace Datasets — miners can upload collected datasets to HuggingFace, making them publicly available in anonymized form.
Participation opportunities in the network:
- Miner:
- Collect data from specific sources (DataSources)
- Store data in a local database
- Provide an index of stored data to validators
- Upload datasets to HuggingFace for public access
- Earn rewards based on the volume and value of stored data
- Validator:
- Periodically query miners to retrieve their data indexes
- Store metadata about all data in the network and which miners hold it
- Verify the correctness of the data stored by miners
- Evaluate miners based on the volume, freshness, and uniqueness of their data
- Distribute rewards among miners
- Consumer:
- Access large volumes of data from various sources through a unified interface
- Use data for training AI models and conducting research
- Receive up-to-date datasets continuously refreshed by miners
- Access unique datasets that may not be available in centralized storage platforms
The scoring system in Data Universe takes several factors into account:
- Freshness of data: newer data is valued more highly, and data older than 30 days is not counted
- Desirability of data: certain types of data are rated higher based on demand
- Duplication factor: data stored by many miners is less valuable than unique data
- Miner reliability: validators check data accuracy and maintain a trust score for each miner
Thus, Data Universe is especially valuable for researchers, AI model developers, and companies that need access to large volumes of diverse data for training machine learning models and conducting analytical research.
The subnet incentivizes data diversity and quality, creating a decentralized infrastructure for storing and accessing information.
You can view the full list of subnets here.